Structural Basis for Marburg Virus Neutralization by a Cross-Reactive Human Antibody
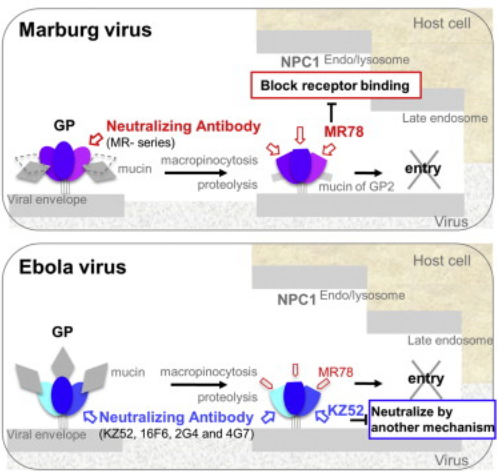
The facilities and staff at the SIBYLS beamline contributed to this recent structural study of a human antibody that is able to neutralize Marburg and Ebola viruses. >The filoviruses, including Marburg and Ebola, express a single glycoprotein on their surface, termed GP, which is responsible for attachment and entry of target cells. Filovirus GPs differ…
Read more