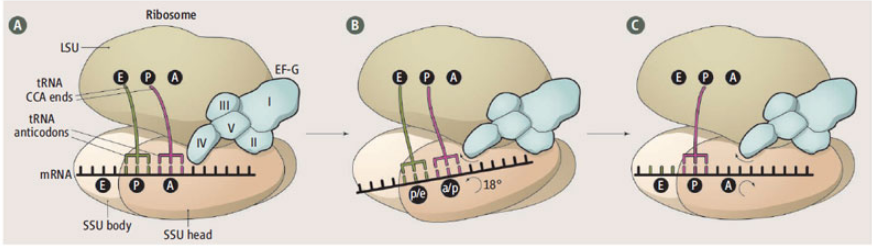
New crystal structures of translocating ribosome
Several new crystal structures of the 70S ribosome in complex with EFG and non-hydrolyzable GTP analogs have revealed how the ribosome directionally translocates mRNA and the tRNAs through the A, P, and E sites and how specific features of EFG and ribosomal RNA act as pawls to enforce this ratcheting mechanism. The new structures were…
Read more