How a Shape-shifting DNA-repair Machine Fights Cancer
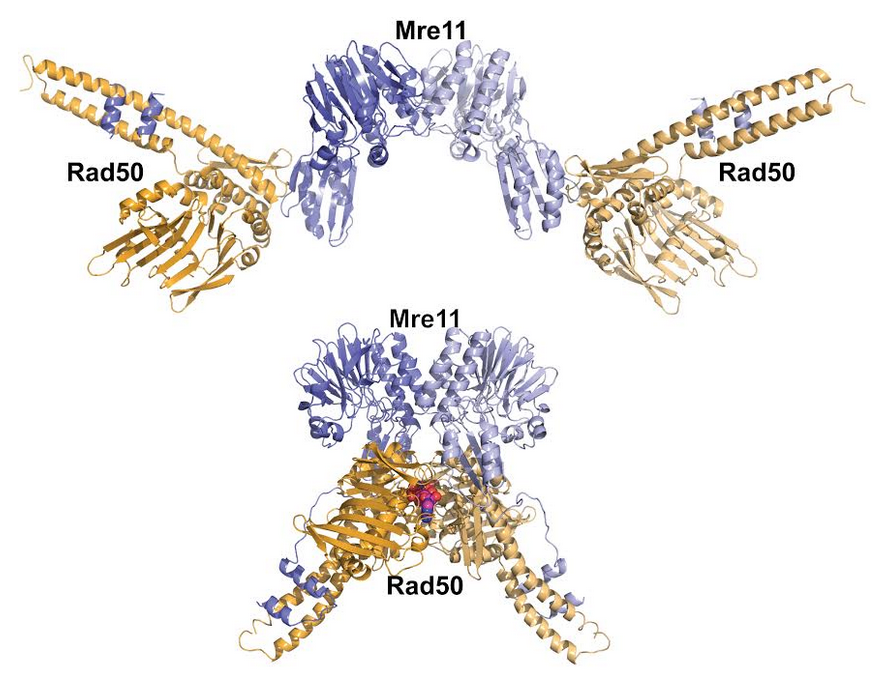
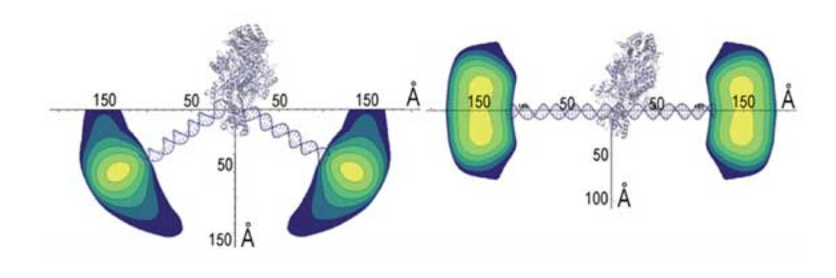
The SIBYLS beamline was instrumental in providing key structural data for two recent publications exploring the dynamic nature of DNA repair. >The Mre11‐Rad50 complex is highly conserved, yet the mechanisms by which Rad50 ATP‐driven states regulate the sensing, processing and signaling of DNA double‐strand breaks are largely unknown. Here we design structure‐based mutations in Pyrococcus…
Read more