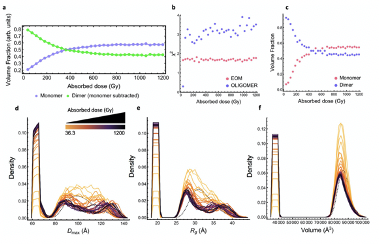
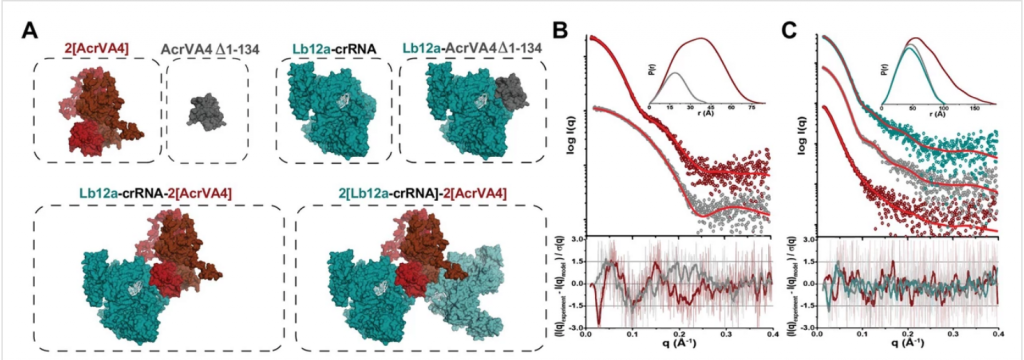
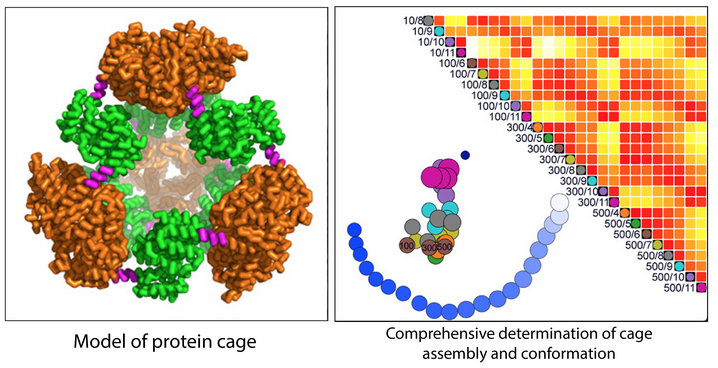
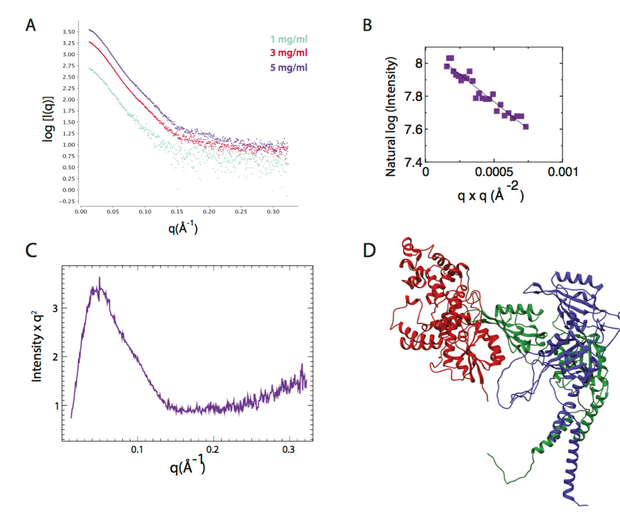
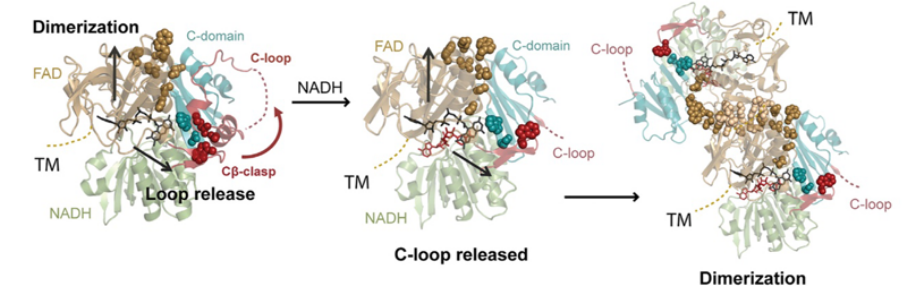
SAXS study of radiation damage
SIBYLS user Dr. Tim Stachowski from the Snell group at Hauptman-Woodward Medical Research Institute, led a research effort combining a protein engineering approach with SAXS to monitor cleavage of a specific bond from exposure to the X-ray beam. X-ray induced disulfide bond breakage is a common phenomenon in X-ray crystallography but there is limited information…
Read more