Evolving SAXS Versatility
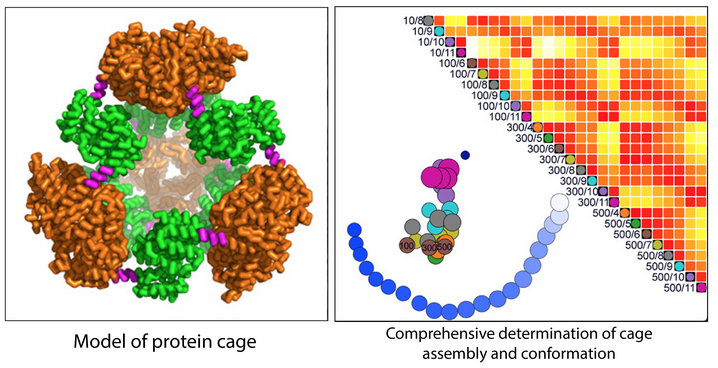
In this top 10 cited article using HT-SAXS data collected at SIBYLS, Chris Brosey, along with John Tainer, describe the value and versatility of Small Angle X-ray Scattering. The authors discuss evolving SAXS theory, methods, and applications that extend the field of small-angle scattering beyond simple shape characterization. From capturing architecture and dynamics to enabling…
Read more